Today's article will be discussing the Process Safety Management standard issued by OSHA. There are 14 element to this standard, we will briefly describe each part and what it entails. So, what is this process safety management standard? Well, according to the site https://www.osha.gov/SLTC/processsafetymanagement/ , this standard is issued to deal with the hazards associated with chemicals that are highly hazardous. What are the components? The 14 components of the standard include process safety information, process hazard analysis, operating procedures, training, contractors, mechanical integrity, hot work, management of change, incident investigation, compliance audits, trade secrets, employee participation, pre-startup safety review, and emergency planning and response. Lets discuss these steps in a little detail. All of this information can be found on the site https://www.osha.gov/Publications/osha3132.html . Process safety information includes having the employee write down all of the hazards associated with the chemicals being used in the process, writing down information about the technology being used in the process and writing down all of the information about the equipment being used in the process. This is done so that employees understand the hazards because they have had to write them down and know them. Process hazard analysis is very similar to process safety information. It is the process of identifying hazards, as well as evaluating and controlling them. The employer is required to use one or more of many methods listed in this site in order to properly evaluate any of the hazards that are being analyzed. Operating procedures includes all of the instructions involved in conducting an operation safely in the workplace. The procedure needs to include the operation phase, operating limits and the health and safety considerations. Training is pretty self explanatory. There must be training done by each employee involved in an operating procedure and refresher training must be done every three years or less. Proper documentation of each employees training record must be kept in order to show that they have received and are keeping up with training. The contractors part of project safety management, or PSM, is stating that contractors employees are to understand that the PSM requirements and safety procedures apply to them even though they may only be there for a short time or for a specialty job operation. Mechanical integrity describes how an employer must keep the equipment up to date and inspected regularly to make sure it works properly. If there are any malfunctions, use on that machinery is prohibited until the problem has been fixed, then further use may continue. A hot work permit is required to be kept on file until the hot work is completed. What is hot work? Well according to the site https://www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/safety_haz/welding/hotwork.html , hot work is when ignitable sources are next to flammable materials. These include cutting and welding. This permit is to describe the fire protection and prevention have been implemented before any hot work is done, the date that the hot work is being done on as well as the location the hot work is being done at. Management of change discusses the procedures that have been written in order to managing changes made to any procedure. This can include chemicals or technology changes. Incident investigation is the process that must occur no later than 48 hours of an incident in order to find the chain reaction of events that happened in order for an incident to occur in the workplace. A list of personnel and task required in this investigation can be found on the site above. Compliance audits states that the last two audits must be kept on file, and also that they are being done at least once every three years to make sure that everything checks out okay. Everything in the audit must be documented. Trade secrets states that an employer must make all information available in order to comply with the PSM. Employee participation is done when the employer makes sure that the employees and representatives are being told the information needed to know that is in the PSM. Pre-startup safety review is when the employer needs to conduct a safety review on a process due to a change in the system, whether that be new procedure or the introduction of a new chemical as well as introducing a new facility into the operation. Lastly, emergency planning and response discusses that the entire employee population at a plant must be aware of the emergency action plan in case of an emergency. This includes the disposal of hazardous chemicals. I hope this article has been helpful in providing information about what the PSM is and what it entails.
Thursday, April 21, 2016
Fire Safety in Labs
Today's article will be all about fire safety in lab. Obviously, laboratories are very dangerous places of work with a lot of hazards, but when you think about fires in a lab, there are so many more dangers involved due to the plethora of chemicals and substances in the lab that can have potential of causing more reactions and explosions when they come into contact with extremely high temperatures. So, what kind of fire safety is there in a lab? Well, according to the site http://www.labmanager.com/lab-health-and-safety/2009/08/laboratory-fire-safety#.VxlaPzjmqP8 , a lot of things can be done in the first place to prevent a fire from even happening. Some of these things include planning out every step of the procedure correctly, store chemicals properly, wear proper PPE, minimize the materials used in the experiment, and not working alone. Of course, the major components to fire safety are all known, that is the PPE, fire extinguishers, and alarms, but there are a few more areas of concern to touch base on. One of these areas is the egress of the lab, that is the way out of the lab. It should be a clear pathway, unblocked, and lead outside to ground level. Another thing to think about when talking about fire safety in labs is the storage of chemicals. This is very important if there is a fire because if the chemicals are properly stored in the appropriate containers, then there may not be the extra hazards of the fire reaching those chemicals. Another thing to think about is that when there is a fire, you want the above sprinkler system to activate to help put out the fire. However, the sprinklers will do no good if they are being blocked by stacked boxes or equipment, so make sure that your sprinkler heads are clear of any blockages that may be in the way. When discussing fire extinguishers, you want to make sure you have the correct one or multiple extinguishers for different fires. You want to make sure you know the PASS technique, which stands for pull, aim, squeeze and sweep. That's how you use a fire extinguisher. Not every fire extinguisher works for every fire. There are different types of extinguishers. According to the site http://www.fire-extinguisher101.com/ , classes A, B, C, and D would all be useful in the laboratory. Class A fire extinguishers are used for fires that are from your ordinary combustibles. These include papers, cardboard and wood. Class B extinguishers are used for combustible liquids, like gasoline or grease/oil. Class C extinguishers are used for any sort of electrical fire. Class D extinguishers are for fires most common in a laboratory most likely. These are fires that from combustible metals, like potassium or magnesium. It is important to know what type of fire extinguishers you have for different fires because they will not work on other types than what they are specified for. Also, some more tips on fire safety can be found on the site http://www.stonybrook.edu/ehs/fire/lab.shtml . Some of the tips include not covering up light bulbs or light fixtures with papers or cloth, not overloading an outlet, and also to be weary of the location of fire safety equipment in your location. I hope this article was helpful in providing some information about fire safety.
Emergency Response
Today's article will be all about emergency response within the laboratory if there is an accident. One source I will be using is information from a packet that I received in class. However, lets look at a different source to start out with. According to the site http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK55874/ , there are four main stages to an emergency response plan. These four stages are the mitigation phase, preparedness phase, response phase and recovery phase. So, what are each of these? The mitigation phase is all about making sure something does not happen, or if something. This includes the proper labeling and storage of materials and chemicals in the lab to make sure they are not being stored dangerously. The preparedness phase is all about being ready if there is an accident that occurs. This can include a lot of things, like making sure that there are personnel on site that can help assist in an emergency, and also making sure that there are first aid and spill kits available. The next phases, response, is all about the efficiency of the staff and outside personnel in case of an emergency. This may be the accessibility of the equipment on site, as well as the knowledge about the substances involved in order to have a better understanding of how to tackle the situation at hand. The last step described by this site is the recovery phase. This is the stage where the quality of the lab can be reviewed to see if there are any areas if improvement in the lab while the lab is being cleaned and washed of the previous accident. If anything can be done better to prevent something from happening again, this is the phase where that is done. According to the site http://www.baylor.edu/ehs/index.php?id=97767 , the emergency response plan should be located near the entrance/ exit of the lab, or by the lab telephone because also on the emergency plan is a list of emergency contacts. This up to date plan should also have written down procedures for a variety of different incidents that can happen in the lab and explain what to do. If there is an spill or accident, try and contain it ONLY if the properties of the chemical have been identified and you are familiar with the hazardous properties of the chemical. If there is a need for evacuation because of an emergency, there needs to be some way that all employees are contacted. This could be some sort of alarm or intercom message. There should also be a procedure for routes to take in case of an evacuation which the employees should already be aware of. Whoever is the emergency contact, if there is a spill, with the assistance of the waste disposal company will determine the status and category in which the waste will be under in order to determine how it will be disposed of. I hope this article was helpful in providing some information to you about the emergency response in labs. It may seem self explanatory, but when there is an accident or emergency it is important for everything to be mapped out, and the plan with the information made available to all employees so that any confusion can be cleared immediately and action can be taken.
Spill Prevention and Control
Today's article will be about the prevention of spills occurring as well as how to control them. We were given a packet to reference from so that will be my min source of information for this article. So, as you can guess spill prevention is pretty self explanatory. However, to make sure that it does not occur, there are a lot of areas tat must be checked and kept up with to make sure that an accident does not happen. For example, the containers where hazardous waste and substances are being stored must be properly sealed, and in compliance to hold the materials within. You don't want to have a corrosive substance in the wrong container because it will eventually make its way through the container due to its chemical properties. Then you have a mess and hazard situation on your hands and if there are other chemicals and hazardous materials around, you may be in an area with a high health and safety hazard. Every container should be CLOSED, and there should be the appropriate signage to indicate what is in the container. Something like "FLAMMABLE" or "HAZARDOUS" or "HAZARDOUS WASTE" signs would be appropriate. The site http://www.labmanager.com/lab-health-and-safety/2010/07/preventing-chemical-spills?fw1pk=2#.Vxk4pDjmqP8 has a few tips as well on how to prevent some spills that happen frequently. A few examples are to place chemicals in the hood to reduce the risk of knocking them over, and also to use absorbent liners at the workbench where the chemicals are being used. Another important thing to know is that chemicals that are being stored in quantities more than 55 gallons should be stored in a secondary container, but this can be used for any sort of chemical or substance that has a high chance of getting spilled or leaked into the environment. In order to make sure that containers are holding chemicals and substances properly, the containers need to be easily accessible by personnel who are going to be inspecting them. It is also good to know that you should not fill drums of chemicals to the very top. There should be at least four inches of space from the top of the container to the top of the chemical in the container. This will prevent and drips or spills if it is to be transported for any reason. According to the site https://www.wright.edu/facilities-management-and-services/environmental-health-and-safety/article/preventing-chemical-spills-in-the-lab , it can also be helpful to conduct a lab as low to the ground as possible, that way if any lab equipment is dropped it may be low enough where it does not crack and leak, creating a potential hazard. Also, this site says that simply knowing and having a good understanding of the chemicals you are working with can be very important because if there is a spill, knowing how to properly dispose and clean it up quickly can prevent the spill from becoming a very dangerous situation. Employees need to be trained for handling hazardous substances as well, and this includes emergency response procedures as well as the spill prevention component of these chemicals. The equipment needed in order to clean up a spill should be easily accessible and employees should know where it is located at all times. These kits should be equipped with the necessary tools needed to clean up the respective chemicals; you don't want a spill kit on site that has equipment needed to clean up a different chemical. I hope this article was helpful in providing some information about spill prevention and control.
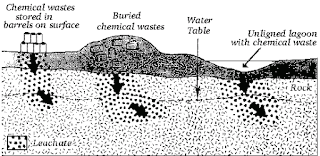
Disposing of Chemical Waste and Unwanted Chemicals
Todays article will be all about the disposing of chemical waste and/or unwanted chemicals. First off lets define exactly what chemical waste is before we get into detail. According to the site http://gogreenplus.org/nuts-and-bolts-guide/planet-nuts-and-bolts-guide/waste-reduction-responsible-disposal/disposing-of-hazardous-waste/ , hazardous waste is any waste that poses a threat to the health of humans or the environment. This waste can be a lot of different things, and come in a lot of forms. This waste can be solid liquid or gas and also it can be in the form of a sludge. Some people, after being in a lab or not, may not be aware that chemicals that are not used in an experiment or for production still need to be disposed of correctly. Even though a chemical is not used, it still can cause serious health affects to humans and the environment. So, what steps should you take of disposing chemicals? Well, according to the site http://smallbusiness.chron.com/dispose-industrial-chemicals-40938.html , the first thing you should do is check the EPA hazardous waste list. The EPA has a list of hazardous wastes that need to be disposed properly, and they also regulate hazardous waste under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act. According to the site https://www.epa.gov/hwgenerators , the EPA regulate hazardous waste based on quantity of business in one calendar month, not how large the company is. The next thing you should do is classify what type of hazardous waste your waste is considered. There are three different categories in which the EPA classifies waste disposal. The category of waste determines how it will be disposed. These three ways of waste disposal, from the site http://smallbusiness.chron.com/dispose-industrial-chemicals-40938.html , are incineration, land disposal and underground injection. Lets talk about each of these a little bit. Incineration is an acceptable way of disposing of hazardous waste as long as the incinerator is up to code with the Clean Air Act. This means that your incinerator can not release any toxins from the incinerating process into the atmosphere. Disposing of hazardous waste on land may seem unsafe and counter productive to this article. Doesn't it seem hazardous? Well, disposing of hazardous waste in landfills is acceptable, if it goes through technological treatments before hand to make it safe to be placed in these landfills. Lastly, you can store waste in an underground injection well. This, along with putting the hazardous waste in a landfill, may seem very unsafe. Why is it okay to put this hazardous waste underground where it can contaminate things? Well, this is acceptable to dispose underground because it is highly regulated. The Safe Water Drinking Act has many regulations when looking at waste disposal and companies who dispose of this waste need to make sure they are in compliance with them in order to inject their hazardous waste deep into the Earth. Also, the Underground Injection Control Program has heavy regulations on this process, to make sure that people disposing of these hazardous materials are doing it properly and following protocol. I hope this article was helpful in providing some useful information to you about disposing of hazardous and unwanted chemicals.
Tuesday, April 19, 2016
Components of Chemical Hygiene Plan
Todays article will be all about the chemical hygiene plan and it's components. Before we go into detail of the components that make up a chemical hygiene plan, lets first discuss what it is. According to the site https://www.osha.gov/pls/oshaweb/owadisp.show_document?p_table=STANDARDS&p_id=10106 , a chemical hygiene plan is a program that is written by the employer that protect employees from hazardous chemicals in specific areas of work. Specifics mentioned in this plan are PPE, or personal protective equipment, and procedures about certain practices in order to keep these employees safe. We were given a sample chemical hygiene plan in class to reference from as well. The components of this sample plan, to be a little bit more specific than what we just mentioned, are first an introduction of what this exact chemical hygiene plan is describing and where it is being executed at. The next step is to write down, in detail, all of the standard operating procedures that are going to be done. This is important because this is where you can see where there is a possibility for hazards to arise. This may be confusing to some people, so lets define what an SOP is. According to the site https://www.bizmanualz.com/save-time-writing-procedures/what-are-policies-and-procedures-sop.html , an SOP, or standard operating procedure is a written step procedure that fully describes all of a plants practices. This has everything from procedures to safety information as well as where things are located in the lab. The next section is stating that the company make's every effort to make sure that it's employees exposure to substances are regulated the best possible and that sampling is done if any levels are found to be over the PEL, or permissible exposure limit. The next component is describing that all employees have fulfilled the proper training necessary to be familiar with such substances and equipment being used, as well as stating that information incase of an exposure is available to them to look at. The medical program component basically states that all employees of the plant who work with hazardous substances have the ability to receive medical attention whenever medical personnel think it is necessary to do any sort of testing, for example if there is someone exposed to a substance and the sample shows the concentration above the PEL, or whenever there is an sort of leak or spill. In our sample, there is a section for special procedures. This components is where practices that require approval are listed, and say who approved them. Hazard identification is the next component to the CHP. This component describes how a company understands that the material safety data sheets, or MSDS are properly filled out and made available to the employees so that they can see the information posted on them if necessary. This contains all sorts of information about the chemicals they are using which is very important to be made easily accessible. The last component of the CHP is to record everything for each employee, medical records, testing, or written statements from them. I hope this article was helpful in providing information about the CHP and its components.
Sunday, April 3, 2016
Cryogenics and Compressed Gases
When talking about occupational health and safety, you may hear of the term cryogenics used. A lot of people may not be aware of what cryogenics means, however and it is very important to understand what this term means when dealing with the safety of employees and everyone around them. According to the site http://www.scienceclarified.com/Co-Di/Cryogenics.html , cryogenics can be defined simply as the studying and production of temperatures that are very low. Now, how low is low when discussing this temperature range? Well, this range, also known as a cryogenic range, is when permanent gases begin to turn from a gaseous state to a liquefied state. And no need to be confused with the term "permanent gas". This simply means elements that are normally identified in a gaseous state. Some examples include nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen and helium. Now that you know what cryogenics is, you are probably wondering what these temperatures actually are. The same sight describes this temperature range to be from about -148 degrees Fahrenheit all the way down to absolute zero. You can make a good guess about what absolute zero is, according to the site https://www.sciencedaily.com/terms/absolute_zero.htm , absolute zero is the lowest temperature possible for anything to be, with heat energy being non-existent within the object. When dealing with compressed gases, understanding what cryogenics is and how it can be applied to the storage of compressed gases is crucial in keeping people safe. What are some of the hazards that can be associated with cryogenics and compressed gases? Well, according to the site https://www.physics.utoronto.ca/physics-at-uoft/services/health-and-safety/cryogenic_safety.html , we can discuss three very good examples of hazards that occur concerning cryogenics and compressed gases. The first one we will discuss is the fact that the environment is extremely cold. This dramatic change of temperature can cause frost bite, if not other injuries that can be equivalent to a third degree burn. So being aware of this and avoiding contact with the gas is very important. Also, the containers that the gases are being stored in may become weak and easily breakable because of the extremely cold temperature. Another thing to be aware of when storing these materials under such conditions is that the extremely cold environment may cause parts of the container to shrink, like caps or nozzles which would then be susceptible to leaking. Another hazard when dealing with cryogenics and compressed gases is asphyxiation. This is basically when there is a gas or other agents that cause impairment to normal breathing and can lead to losing consciousness or even death. Lastly a third risk of cryogenics and compressed gases is dealing with pressure of the containers that the gases are being stored in. Under these conditions, the proper pressure needs to be attained or else the pressure of the container will eventually cause an explosion which can lead to serious injury as well as cause a chain reaction from the explosion. I hope this blog was helpful in providing some information to you about dealing with cryogenics and compressed gases and will help you be more aware of the possible hazards that can be easily looked over when dealing with these conditions.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)